Having good health is necessary for living a happy life. The early identification and prevention of potential health problems are greatly aided by routine health screening exams. It is crucial that adults take responsibility for their health and get regular checkups. This thorough guide will cover the necessity of routine health screening exams for adults, as well as the various exams, their importance, and how they support maintaining general health.
Importance Of Regular Health Screening
Regular health exams are crucial for several reasons
- Early Detection: Health checks can spot problems with your health when they're still treatable and manageable.
- Prevention: Health screenings help people identify risk factors so they can adjust their lifestyles and take preventive action.
- Risk assessment: Based on a person's family history, lifestyle, and other characteristics, screening tests can help determine how likely they are to get a particular disease.
- Better control: Early chronic illness discovery lowers the risk of complications and allows for better control of the condition.
- Peace of Mind: Having regular health screenings gives you peace of mind because you know that you are protecting your health in a proactive manner.
Essential Screening For Adults
Adults must undergo routine health screenings to keep track of their health and identify any problems before they become serious. These screens aid in the early diagnosis and prevention of a number of diseases, which improves quality of life and health outcomes. Adults should routinely undergo the following vital health screening tests:
1. Blood Pressure measurement
Taking one's blood pressure is a basic screening procedure to evaluate cardiovascular health and determine the likelihood of hypertension. Significant risk factors for heart disease, stroke, and other health issues include high blood pressure.
2. Cholesterol panel
A cholesterol panel measures multiple blood levels of cholesterol, including triglycerides, LDL (low-density lipoprotein), and HDL (high-density lipoprotein). This examination assesses both the risk of developing heart disease and the state of the heart.
3. Blood Glucose Test
A blood glucose test measures blood sugar levels and is crucial for identifying and controlling diabetes. High blood sugar levels may be a sign of diabetes or prediabetes, which call for prompt treatment and dietary adjustments.
4. Complete urine test
Urinalysis, often known as a full urine examination test, is a typical diagnostic procedure that examines the physical, chemical, and microscopic characteristics of urine. It is a simple, non-invasive test that offers insightful data about a person's general health and aids in the early identification of a number of medical disorders.
5. Thyroid profile test
A series of blood tests known as a thyroid profile exam, sometimes referred to as thyroid function tests, evaluate the condition and operation of the thyroid gland. Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) are the two main thyroid hormones that are produced by the thyroid gland, which is in the front of the neck. The creation of energy, metabolism, and general growth and development all depend on these hormones.
6. Vitamin B12 serum test
The serum cobalamin test, sometimes referred to as the vitamin B12 serum test, is a blood examination that gauges the amount of vitamin B12 present in the body. The generation of red blood cells, DNA synthesis, neuron function, and energy production are just a few of the processes that vitamin B12 is vital for.
7. X-ray chest PA view
A diagnostic imaging examination called a posteroanterior (PA) view chest X-ray produces a two-dimensional image of the chest region. To produce an image of the chest structures, such as the lungs, heart, ribs, and surrounding tissues, the X-ray machine emits a little quantity of radiation.
8. Liver function test
A series of blood tests known as a liver function test (LFT) are used to evaluate the liver's condition and capacity. The liver is a crucial organ that performs a number of key bodily processes, including the metabolism of nutrients, the detoxification of toxic chemicals, the production of bile for digestion, and the storage of energy in the form of glycogen.
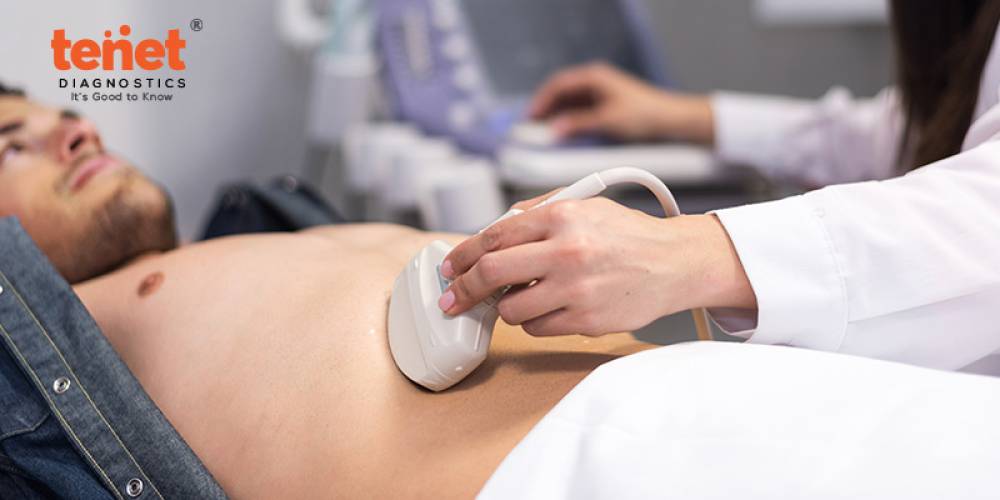
9. Ultrasound whole abdomen
A non-invasive imaging procedure called an abdominal ultrasound, also called an abdominal sonography, employs sound waves to provide real-time images of the organs and structures inside the belly. It is a useful diagnostic tool for examining a number of abdominal organs, including the kidneys, spleen, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
Final Words
An essential component of preventative healthcare is routine health screenings. They enable the early identification of prospective health issues by offering insightful information about a person's current state of health. Adults can prioritize their well-being and live better lives by being proactive and collaborating closely with healthcare experts. Always remember that prevention is always preferable to treatment, and routine medical exams can even save lives.