It has never been more critical to keep knowledgeable about your heart health in a world where cardiac disorders are on the rise. The Cardiac Profile Test is a valuable instrument for evaluating your cardiovascular health. Understanding what this test includes is essential whether you are proactively monitoring your heart health or have been instructed to do so by your doctor.
In this extensive article, we will go deeply into the world of Cardiac risk Profile Tests so that you can fully understand what they are, why they are essential, and what to expect throughout the test. We'll review the test's numerous components, its importance in identifying heart issues, and how it might play a significant role in your quest for general health and wellness.
Cardiac Profile Test at Tenet Diagnostics
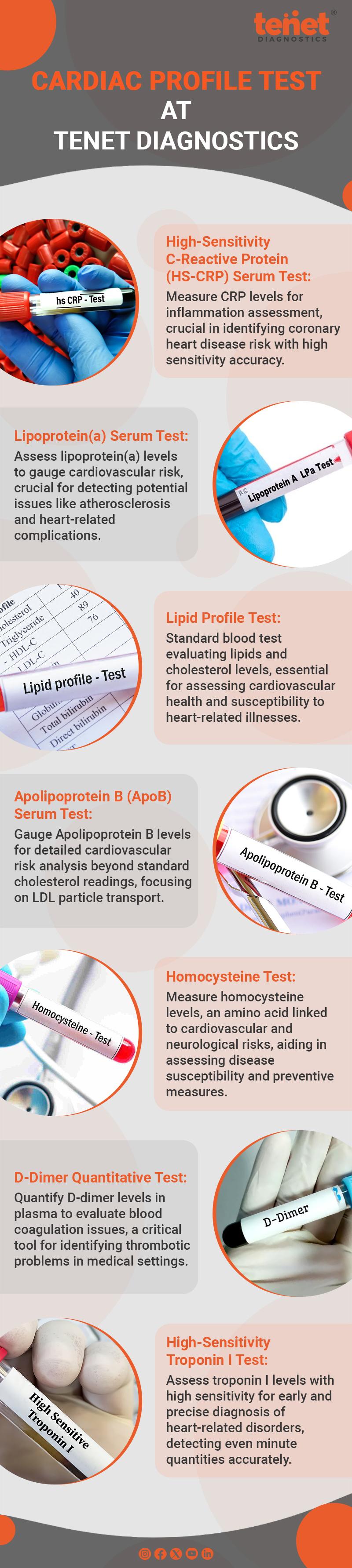
1. High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein (HS-CRP) Serum Test
The High-Sensitivity C-reactive protein (HS-CRP) Serum Test is a blood examination that gauges your body's levels of a particular protein called C-reactive protein (CRP). Your liver produces CRP in reaction to bodily inflammation, especially in the arteries. This test's "high sensitivity" feature allows it to accurately identify risk, which makes it a valuable tool for determining the likelihood of coronary heart disease and other inflammatory diseases.
2. Lipoprotein(a) Serum Test
The Lipoprotein(a) Serum Test, often known as the Lp(a) Test, is a blood test that gauges your body's levels of a particular kind of lipoprotein called lipoprotein(a). Apolipoprotein(a) is a protein component combined with a lipid core to form a distinct cholesterol particle known as lipoprotein(a). An increased risk of cardiovascular illnesses, particularly atherosclerosis, heart attacks, and stroke, has been linked to elevated levels of Lp(a).
3. Lipid Profile Test
The Lipid Profile Test, often known as a "lipid panel" or "cholesterol blood test," is a standard blood test in cardiac checkup package that gives essential details on the concentrations of different lipids (fats) and cholesterol in your blood. This examination is valuable for evaluating cardiovascular health and pinpointing your vulnerability to heart-related illnesses, including heart disease and stroke.
4. Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) Serum Test
The Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) Serum Test is a blood examination that gauges your body's Apolipoprotein B levels. The protein apolipoprotein B is essential in transporting cholesterol and other fats in the blood, especially within low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles. This test helps determine cardiovascular risk by giving more details than standard cholesterol readings.
5. Homocysteine Test
The Homocysteine Test is a blood test used to gauge your body's homocysteine levels. Homocysteine is an amino acid created to break down proteins in your body. However, raised blood homocysteine levels have been linked to a higher risk of several diseases, including cardiovascular disease and some neurological illnesses.
6. D-Dimer Quantitative Test
A blood test known as the D-Dimer Quantitative Test uses sodium citrate plasma to quantify the amount of a chemical known as D-dimer in the bloodstream. When blood clots dissolve, a fragment known as D-dimer is created. This test is primarily used in medical settings to evaluate and identify thrombotic and blood coagulation problems.
7. High-Sensitivity Troponin I test
A High-Sensitivity Troponin I test assesses the blood's protein level known as troponin I. A cardiac biomarker called troponin I is released into the blood when the heart muscle is damaged, as occurs after a heart attack or other cardiac events. This cardiac profile test's high-sensitivity variant can diagnose heart-related disorders early and more accurately by detecting even highly minute quantities of troponin I in the blood.
Infographic: Cardiac Profile Test
Who needs to undergo the cardiac profile test
You might need this test if your doctor suspects you have or has recently had a heart attack. If you experience the signs of a blocked coronary artery, you might also require a cardiac evaluation test. Other factors include:
1. Age and gender
Heart disease is typically more common in males and women over 45 and 55, respectively. In these age ranges, routine TMT cardiac testing is frequently advised. It may also be recommended to start testing earlier for younger people with specific risk factors or a family history of early heart disease.
2. Pre-existing Illnesses
Regular cardiac package testing may be necessary to monitor the heart health of people with medical disorders that increase their risk of heart disease, such as diabetes, high blood pressure (hypertension), high cholesterol, or obesity.
3. Lifestyle variables
Cardiac evaluation test can help inactive people who smoke, have bad eating habits, or drink too much alcohol determines their risk of developing heart disease and get advice on changing their lifestyles.
Final Words
We have revealed the critical information concerning this vital heart health screening tool in this thorough investigation of the Cardiac Profile Test. We've taught you to take charge of your cardiovascular health, from comprehending its significance to figuring out the many components. With the help of the Cardiac Profile Test, you can monitor and control potential risks even before symptoms show up, providing a crucial window into the health of your heart. This test can offer insightful information and direct your healthcare choices, whether you're actively protecting your heart or attending to specific issues.